HCI (Human Computer Interaction) is the study of how humans use computers and other digital devices. It explains the relationship between people and machines. When you give instructions to a computer and it responds, this process is called HCI.
HCI is important because it makes technology easier for everyone. When you use your phone, play games, or search the internet, you are experiencing HCI. For example, pressing icons on a smartphone or withdrawing money from an ATM are common forms of human-computer interaction.
Basic Concepts of HCI
The main idea of HCI is interaction. Interaction means a two-way communication. In this case, the communication is between the user and the computer. The user gives instructions, and the computer shows the result.
For example, when you click a mouse button, you are giving input. The computer processes this input and shows something on the screen. That result is the output. Input and output work together to make communication possible.
Input Devices like:
- Keyboard
- Mouse
- Touchscreen
- Microphone
Output Devices like:
- Monitor
- Printer
- Speakers
- Headphones
Goals of Human Computer Interaction
The primary goal of HCI is to make computers intuitive and user-friendly. Some key goals are:
1. Ease of Use
The first goal of HCI is ease of use. A computer system should be simple enough that even a beginner can use it. For example, a smartphone with clear icons and menus is easy to use. Users do not need special training. They can open apps, make calls, or send messages quickly.
2. Better User Experience (UX)
Another important goal is a better user experience. User experience is also called UX. It means how a person feels while using a computer or device. If the design is smooth and friendly, users feel happy and confident.
For example, when you use a learning app with a clean layout and fast performance, you enjoy studying more. On the other hand, a confusing app makes you frustrated.
3. Fewer Errors
HCI also aims to reduce errors. Mistakes happen when a system is not clear. For example, if two buttons look the same, a user may press the wrong one. A well-designed system guides the user step by step and prevents such errors.
Some systems also show warnings, like “Are you sure you want to delete this file?” This extra step prevents mistakes. Reducing errors saves time, avoids stress, and builds trust between humans and computers.
4. Saving Time
Another goal of HCI is to save time. A good system allows users to complete tasks quickly. For example, searching for a file with one click is faster than going through many menus. In online forms, features like auto-fill also save time.
5. Accessibility
Accessibility is one of the most important goals of HCI. This means that everyone, including people with disabilities, should be able to use technology. For example, people with weak eyesight can use screen readers. While people who cannot type can give voice commands. HCI makes sure that no one is left out.
Components of HCI
Human-Computer Interaction is made up of three important parts. These parts are the user, computer, and interaction. All three are necessary. Let us study them one by one.
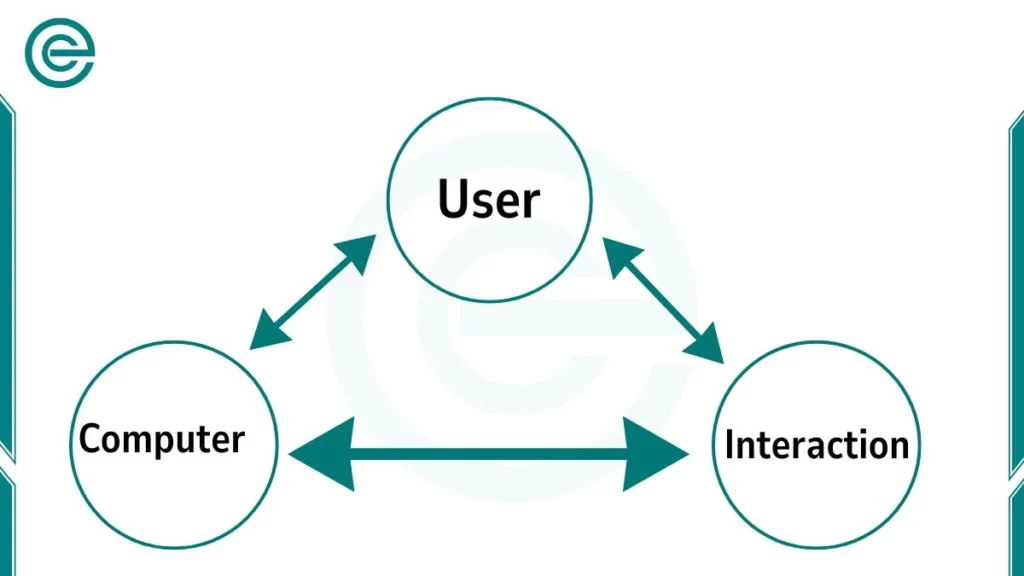
1. User
The user is the human being who operates the computer. This can be a student, a teacher, a doctor, a businessperson, or even a child. Every user has different skills and knowledge. Some users are experts, while others are beginners.
2. Computer
The computer is the machine that receives the instructions and gives back the results. It has three main parts: hardware, software, and the operating system.
Hardware means the physical parts of the computer. Software means the programs and applications that perform specific tasks, like Microsoft Word or Google Chrome. The operating system connects the hardware and software. It controls how they work together and manages all the activities.
3. Interaction
The third part is the interaction itself. This is the actual communication between the user and the computer. Interaction happens through input and output devices. For example, when you type a word on the keyboard, that is input. When the word appears on the screen, that is output.
Areas of Human Computer Interaction
HCI covers many types of interfaces:
- Graphical User Interfaces (GUIs): A Graphical User Interface uses windows, icons, menus, and buttons. You see it on desktops, laptops, and most apps. You point and click to perform actions. You drag files, open folders, and press on-screen controls. It feels natural because you work with visual objects.
- Command Line Interfaces (CLI): A Command Line Interface uses text commands. You type instructions, and the computer runs them. You see this in the Terminal on Linux and macOS, and Command Prompt or PowerShell on Windows.
- Touch and Gesture Interfaces: Touch and gesture interfaces appear on smartphones, tablets, kiosks, and interactive boards. You tap, swipe, pinch, and zoom with your fingers. The screen reacts to your gestures in real time.
- Voice Interfaces: Voice interfaces let you speak to the computer. You ask a question, give a command, or dictate text. Systems like Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant follow your words and reply with speech or actions.
This interface is helpful when your hands are busy. It supports accessibility for users who cannot type or see well. - Virtual Reality (VR): Virtual Reality places you inside a digital world. You wear a headset and look around a 3D space. You move, select, and explore using controllers or hand tracking. It is strong for games, training, and simulations. It supports safe practice for risky tasks, such as lab work or industrial steps.
Applications of HCI in Real Life
Human-Computer Interaction is everywhere around us. Some examples include:
- Education: HCI plays a big role in modern learning. Smartboards make classrooms interactive. E-learning platforms allow students to study from anywhere. Online classrooms give teachers and students a chance to connect in real time.
- Healthcare: Hospitals and clinics use HCI systems every day. Patient record systems help doctors store and check medical history quickly. Telemedicine apps let patients talk to doctors without visiting the hospital.
- Business: Offices depend on HCI for smooth work. Tools like Microsoft Office or Google Workspace help in creating documents and presentations. Online meeting platforms like Zoom or Teams make communication fast.
- Gaming: The gaming world uses advanced HCI. VR headsets give players a real-life experience of the game. Game consoles provide easy controls for entertainment. Motion sensors allow players to use body movements in games.

