Hybrid topology is a type of network topology that combines two or more different types of topologies, such as star, bus, and ring, to create a flexible and scalable network structure. It is useful in large networks where a single topology is not enough. It allows networks to be designed based on the specific needs of an organization.
What is Hybrid Topology in Computer Networks?
A hybrid topology is a network that integrates multiple basic topologies into a single network. This combination makes it possible to customize the network layout to suit specific needs. Hybrid topology is important in networking because it offers the best of multiple topologies while addressing the limitations of using just one.
For example: A hybrid network might combine a star topology with a bus topology, or a ring topology with a mesh topology.
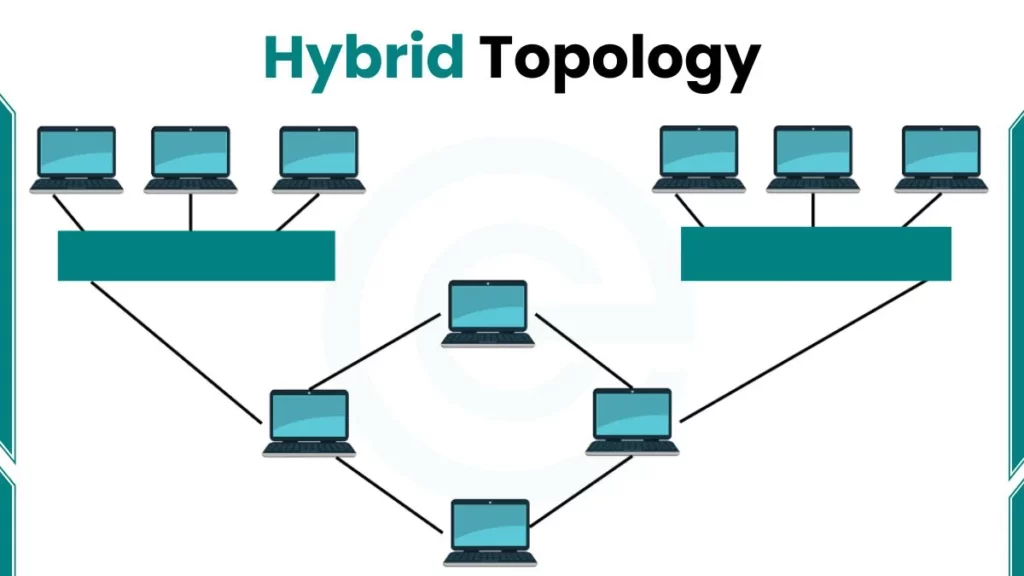
Types of Hybrid Topologies
The following are the types of Hybrid Topology:
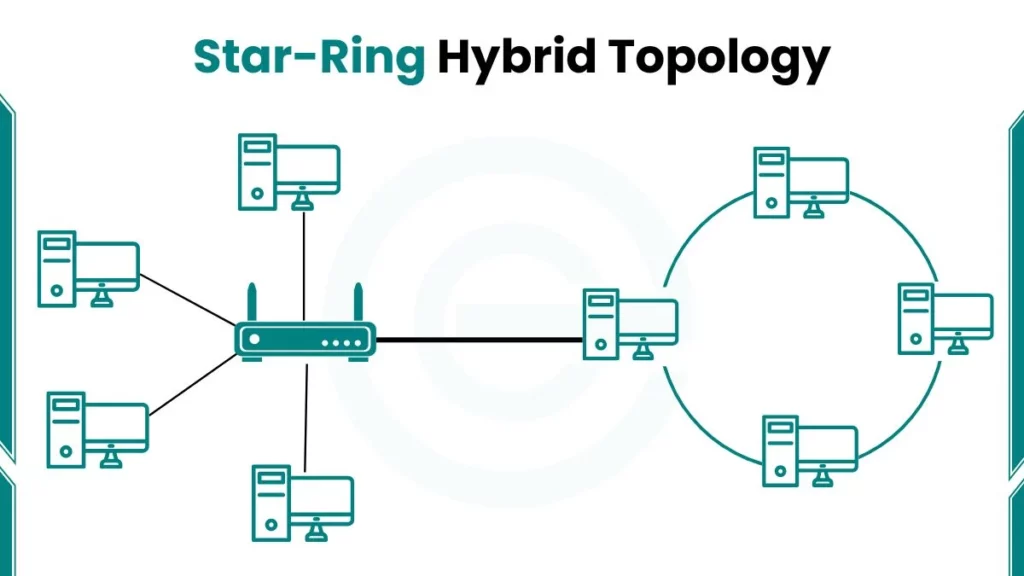
1. Star-Ring Hybrid Topology
The two most common topologies “star topology and ring topology” are combined in the star-ring hybrid topology. The star topology connects computers or devices to a central hub, while the ring topology connects devices in a circular format. This combination creates a stable network that can handle high volumes of data.
- Characteristics: Easy to troubleshoot, stable data flow.
- Use Cases: Corporate networks with stable data transmission needs.
2. Star-Bus Hybrid Topology
This hybrid topology combines a star topology’s central hub design with a bus topology’s linear structure. The star-bus hybrid allows for multiple devices to be connected to a central hub, and the hub connects to a bus backbone.
- Characteristics: High fault tolerance, easy to expand.
- Use Cases: Networks that need scalability, such as university campuses.
Advantages of Hybrid Topology
Hybrid topologies offer several benefits that make them ideal for many networks. Here are the key advantages:
- Flexibility in Design: Hybrid topology allows for using different structures within a single network, making it flexible in design and application.
- Fault Tolerance: If one part of the network fails, other parts can continue to function. This makes hybrid topology more fault-tolerant than single topology structures.
- Scalability: It’s easy to add new nodes or devices to the network. This makes it ideal for growing organizations.
- Enhanced Performance: Hybrid topology can support high-speed data transfer and better network performance, especially for large networks.
Disadvantages of Hybrid Topology
Despite its many advantages, hybrid topology also has some drawbacks:
- Complex Design: The design and setup of a hybrid topology are often more complex than single topologies. It requires careful planning and expertise.
- Higher Cost: The setup and maintenance of hybrid topologies can be expensive due to the need for more advanced hardware and installation processes.
- More Points of Failure: While hybrid topology improves fault tolerance, the combination of different topologies can also introduce more points of failure, making troubleshooting harder.
Read more details about advantages and disadvantages of a hybrid topology.
Applications of Hybrid Topology
Hybrid topology is used in many real-world applications. Especially where large and complex networks are required.
- Corporate Networks: In large corporations, a hybrid topology is used to manage vast networks spread over different locations. Combining different topologies allows for better control and flexibility.
- Educational Institutions: Many universities and schools use a hybrid topology to connect multiple buildings and departments. This helps maintain high-speed connections for critical systems while allowing affordable solutions for smaller areas.
- Data Centers: Hybrid topologies are also used in data centers, where a mix of topologies is required to handle large amounts of traffic.
Why Organizations Choose Hybrid Topology
Organizations prefer a hybrid topology because it allows them to customize their network to fit specific needs. Whether they need high fault tolerance, scalability, or flexibility, a hybrid topology offers a solution that can adapt to changing requirements. Educational institutions often use hybrid networks to support large numbers of students and staff while ensuring that the network is easy to expand as the institution grows.

