Tree topology is also known as hierarchical topology. It is a fundamental concept in computer networks and data structures.
What is Tree Topology?
Tree topology is a network structure that resembles a tree’s branching pattern. In this arrangement, network devices are connected hierarchically with a central node (root) at the top and other nodes branching out below it. This structure allows for efficient data flow and organization within a network.
Tree Topology Definition
A tree topology can be defined as a network architecture where multiple nodes are connected in a branching hierarchy, starting from a single root node. Each node, except the root, has one parent node and can have multiple child nodes. This creates a structure resembling an inverted tree.
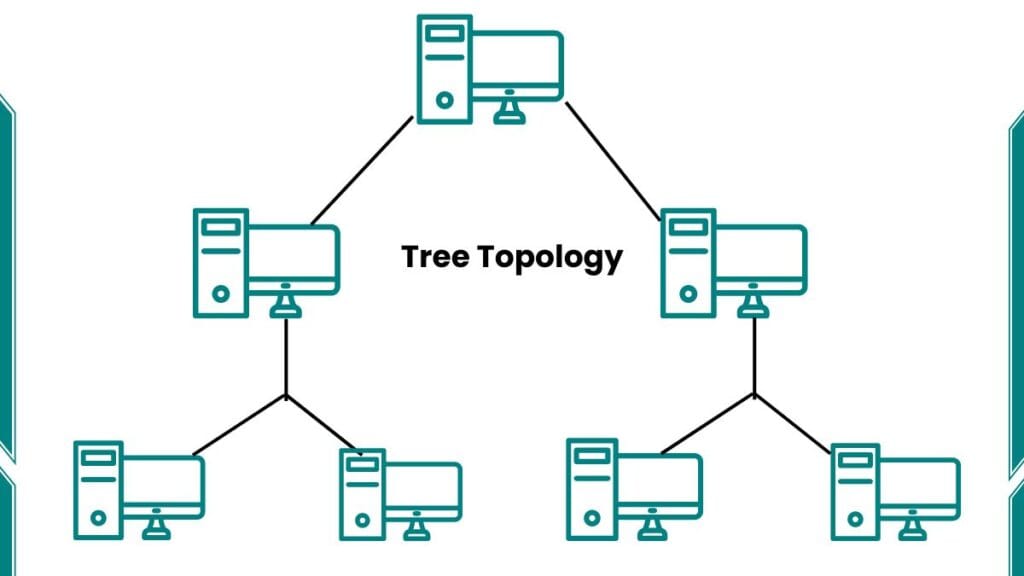
Types of Tree Topology
There are different types of tree topologies including:
- Binary Tree: Each node has a maximum of two child nodes.
- Ternary Tree: Each node can have up to three child nodes.
- N-ary Tree: Each node can have any number of child nodes.
- Fat Tree: A special type used in data centers for improved performance.
Network Tree Topology Examples
Tree topologies are commonly used in various network setups. Some examples include:
- Corporate networks: Large companies often use tree topologies to organize their departments and branches.
- Cable TV networks: The signal is distributed from a central location to various neighborhoods and then to individual homes.
- File systems: Computer file systems often use a tree structure to organize folders and files.
How Does Tree Topology Work?
In a tree topology, data flows from the root node down through the branches to the leaf nodes (nodes without children). Here’s a simple breakdown of how it works:
- Main Device: There’s one main device at the top, like the grandparent of the family.
- Connected Devices: Other devices connect to this main one, like children in a family.
- More Connections: These ‘child’ devices can have their connections, like grandchildren.
- Branching Out: This keeps going, with each device potentially connecting to more devices below it.
- One-Way Connections: Each device (except the main one) only connects to one device above it, just like how a child has one set of parents.
- Many Lower Connections: Each device can connect to many below it, like how parents can have many children.
- Tree-Like Shape: When you draw this out, it looks like a tree turned upside down.
This hierarchical structure allows for efficient data transmission and helps manage large networks.
Advantages and Disadvantages of a Tree Topology
Here are some tree topology advantages and disadvantages:
Advantages
- Easy expansion: New nodes can be added easily.
- Efficient management: The hierarchical structure makes it easier to manage and troubleshoot.
- Scalability: It can accommodate a large number of devices.
Disadvantages
- Single point of failure: If the root node fails, it affects the entire network.
- Cable length limitations: As the network grows, cable length can become an issue.
- Complexity: Large tree networks can become complex to maintain.
Tree Topology in Computer Networks
In computer networks, tree topology is a popular choice for organizing and connecting devices. It combines elements of star and bus topologies creating a hybrid structure that’s both flexible and scalable.
