An analog signal is a type of signal that is continuous. This means it can have any value within a range. For example, when you speak into a microphone, your voice is converted into an electrical signal. This signal is analog because it changes smoothly over time. It does not have sudden jumps or breaks.
Definition of Analog Signal
An analog signal is a continuous wave that varies over time. It can take any value within a given range. For example, if you look at a sound wave, it goes up and down smoothly. This smooth change is what makes it an analog signal. Sound waves, temperature variations, and pressure changes are common examples of real-world data represented using analog signals.
If you want to explore how these signals appear in everyday devices, you can read a guide on examples of analog signals.
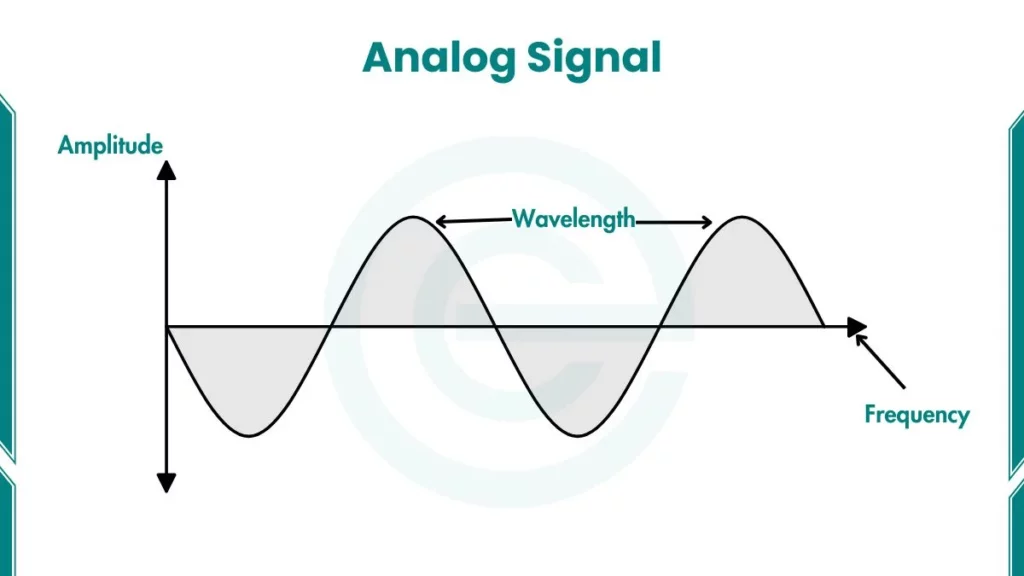
Characteristics of Analog Signals
Analog signals have three main characteristics. Here are the analog signal characteristics:
1. Amplitude
Amplitude is the height of the signal. It represents the strength or volume of the signal. For example, in a sound wave, the amplitude determines how loud the sound is.
2. Frequency
It is how often the signal repeats in one second. It is measured in Hertz (Hz). For example, if a signal repeats 50 times in one second, its frequency is 50 Hz. Frequency determines the pitch of a sound. A high-frequency signal produces a high-pitched sound, while a low-frequency signal produces a low-pitched sound.
3. Phase
It is the starting point of the signal. It tells us where the signal begins in its cycle. Phase is important when combining multiple signals. If two signals have the same frequency but different phases, they can cancel each other out or amplify each other.
These characteristics are fundamental to understanding the difference between analog and digital signals, where digital signals are discrete and quantized.
How Analog Signals Work
Analog signals are generated by devices like microphones, sensors, and antennas. For example, a microphone converts sound waves into electrical signals. These signals are then transmitted through wires or air.
When the signal reaches its destination, it is converted back into sound, light, or another form. For example, a speaker converts electrical signals into sound waves. This process is called signal transmission and reception.
In communication systems, analog signals are often modulated before transmission. Modulation means changing the signal so it can travel long distances. At the receiving end, the signal is demodulated to recover the original information.
Analog Signal Processing
Analog signal processing involves modifying analog signals. Common techniques include amplification, filtering, modulation, and demodulation.
- Amplification increases the strength of the signal. This is useful when the signal is weak, such as after travelling a long distance.
- Filtering removes unwanted frequencies from the signal. For example, a low-pass filter allows low frequencies to pass while blocking high frequencies.
- Modulation changes the signal so it can travel long distances. For example, in radio broadcasting, the audio signal is modulated onto a carrier wave.
- Demodulation recovers the original signal from the modulated signal. This is done at the receiving end of a communication system.
Mathematical Representation of Analog Signals
Analog signals can be represented mathematically. The most common representation is a sine wave. The equation for a sine wave is:
y(t)=A sin(2πft+ϕ)y(t)=A sin(2πft+ϕ)
In this equation, A is the amplitude, ff is the frequency, and ϕϕ is the phase. The variable tt represents time.
For example, if the amplitude is 5, the frequency is 2 Hz, and the phase is 0, the equation becomes:
y(t)=5 sin(2π×2×t+0)y(t)=5 sin(2π×2×t+0)
This equation helps us understand how the signal changes over time. By adjusting the amplitude, frequency, and phase, we can create different types of signals.
Applications of Analog Signals
Analog signals are used in many real-world applications:
1. Audio Systems
Analog signals are used in many real-world applications. One common use is in audio systems. Vinyl records and analog radios use analog signals to produce sound. When you play a vinyl record, the needle reads the continuous grooves on the record, representing the analog signal.
2. Television Broadcasting
Another application is in television broadcasting. Older TVs used analog signals to display images and sound. The signal was transmitted through the air and received by an antenna on the TV.
3. Sensors
Sensors also use analog signals. For example, a thermometer measures temperature and produces an analog signal. This signal can be displayed on a dial or converted into a digital reading.
4. Communication Systems
Communication systems, like landline telephones, use analog signals to transmit voice. When you speak on a telephone, your voice is converted into an analog signal and sent through the phone line.
For a structured breakdown of where analog signals are used, read out the uses of analog signals article.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Analog Signals
The following are the Advantages and Disadvantages of Analog Signals:
Advantages
- High Precision: Analog signals can represent data with high accuracy.
- Simple Design: Analog devices are often simpler and cheaper to build.
- Better for Certain Applications: Analog signals are better for audio recording and natural data representation.
Disadvantages
- Noise and Interference: Analog signals are easily affected by noise, which can distort the signal.
- Limited Range: Analog signals weaken over long distances.
- Storage and Processing: Storing and processing analog signals is harder than digital signals.
For a complete and detailed explanation, you can read our guide on advantages and disadvantages of analog signals.
FAQs
What is an Analog Signal in Digital Electronics?
In digital electronics, an analog signal is a continuous signal that represents physical measurements. It can have any value within a range. Digital electronics often convert analog signals into digital signals for processing. For example, a temperature sensor produces an analog signal, which is then converted into a digital signal by an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) for use in digital systems.
What is an Analog Signal in Computer Networks?
In computer networks, an analog signal is used to transmit data over communication channels. For example, older modems used analog signals to send data over telephone lines. The analog signal carries the digital data by modulating it onto a carrier wave. At the receiving end, the analog signal is demodulated to recover the original digital data.
Why are analog signals still used today?
Analog signals are better for certain applications, like audio recording and sensors. They are also simpler and cheaper to build in some cases.
