Multimedia is the integration of multiple forms of media such as text, images, audio, video, and interactive elements. It has evolved from the traditional single-medium formats to a more dynamic and interactive form of communication where different multimedia types are combined to convey information more effectively.
Multimedia has become an essential part of our daily lives from educational videos on YouTube to interactive websites and video games. It’s a powerful tool for communication, education, entertainment, business, healthcare, and many other fields.
Categories of Multimedia
Multimedia can be largely categorized into two main types based on how users interact with it:
1. Linear Multimedia
Linear multimedia is a non-interactive form where the user passively consumes the content in a predetermined order. Examples include movies, music, slideshows, and non-interactive e-books. The user has no control over the sequence or flow of the information.
2. Non-Linear Multimedia
Non-linear multimedia also known as interactive or hypermedia. It allows users to control their own experience by navigating through the content non-sequentially. Examples include websites, video games, and interactive tutorials. Users can interact with the content through hyperlinks, buttons, menus, or other interactive elements.
Both linear and non-linear multimedia have their advantages depending on the context and purpose. Linear multimedia is well-suited for storytelling, entertainment, and passive learning while non-linear multimedia is ideal for interactive learning, exploration, and problem-solving.
Components of Multimedia
Multimedia is formed of some key components. Here are these multimedia components:
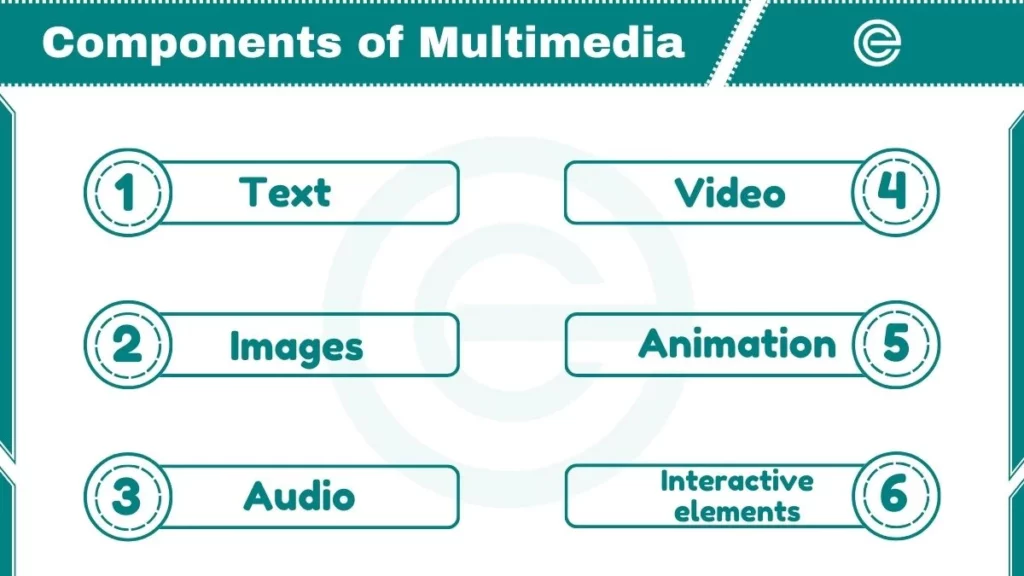
1. Text
Text is written information that provides context, instructions, or additional details. It can range from short captions to longer passages. It can be used to guide the user through the multimedia experience. Clear and concise writing is important for effective communication in multimedia content.
2. Images
Images including photographs, illustrations, diagrams, and other visual elements to enhance understanding and visual attraction. They can convey complex ideas or emotions more effectively than text alone. Visuals can grab attention and make complex information more accessible.
3. Audio
Audio elements such as music, sound effects, narration, or other audio elements add atmosphere and depth to the knowledge. They can set the mood, provide a sense of place, or even convey information directly. Different types of audio can be used to create specific emotional responses or set the tone for the content.
4. Video
Video combines moving images with sound making it a strong medium for conveying complex ideas or emotions. It can create engaging reports, demonstrate processes, or provide more immersive knowledge. Live-action and animated videos can be used in a group of multimedia applications.
5. Animation
Animation is computer-generated graphics often used to create dynamic and engaging visual effects. It can be used to bring static elements to life or to create fully new worlds and characters. Different animation techniques such as 2D, 3D, and stop-motion can create unique visual effects and tell stories in stunning ways.
6. Interactive elements
Interactive elements such as hyperlinks, buttons, menus, and other interactive components allow users to control their experience and navigate through the content. They can provide a sense of instrumentation and engagement. It can be used to personalize the experience.
Each component is crucial in creating an immersive and interactive multimedia experience.
Applications and Uses of Multimedia
Multimedia use in different fields. Here are some applications and uses of multimedia in different fields:
- Education: E-learning platforms, interactive presentations, and educational videos make learning more engaging and effective.
- Entertainment: Movies, video games, music, and other forms of entertainment often combine multiple media forms to create stunning pieces of knowledge.
- Business: Marketing campaigns, advertising, and employee training programs use multimedia to communicate effectively.
- Communication: Social media, video conferencing, and other communication tools use multimedia to enhance collaboration and information sharing.
- Art and design: Digital art, animation, and interactive installations use multimedia to create unique and creative words.
- Healthcare: Medical simulations and patient education programs use multimedia to improve understanding and provide more effective healthcare.
- Science and research: Data visualization, simulations, and other scientific applications use multimedia to make complex concepts more accessible.
Benefits of Using Multimedia
Multimedia enhances communication and learning by:
- Increased engagement and interactivity: The combination of different media forms creates a more captivating and interactive experience compared to traditional single-medium formats.
- Catering to different learning styles and preferences: Multimedia can accommodate a wide range of learning styles from visual to hearing to hands-on learning.
- More memorable and impactful information delivery: Multimedia can make information more memorable and impactful by engaging multiple senses and creating a more immersive experience.
Real-world examples of effective multimedia use include educational videos that combine text, visuals, and narration to explain complex concepts. Interactive museum exhibits that engage visitors through a combination of visual, auditory, and tactile elements. And marketing campaigns that use a mix of video, animation, and interactive elements to capture attention and drive engagement.
Future of Multimedia
Arising trends in multimedia technology include:
- Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR): These technologies create immersive experiences that blur the line between the digital and physical worlds.
- Artificial intelligence (AI): AI can be used to personalize multimedia content and create more intelligent and responsive experiences.
- Personalized content and experiences: Customized multimedia content tailored to individual preferences and needs.
- Immersive storytelling: Innovative techniques that create a sense of being “inside” the story enhancing emotional impact and engagement.
These trends will shape multimedia’s future, making it even more interactive, personalized, and engaging.
Also Read:
| Multimedia Programming-APIs, Scripting, and Frameworks | Multimedia File Formats-Image, Audio, Video and Extensions |
Related FAQs
List of 3 multimedia software examples
Multimedia software examples include:
1. Adobe Photoshop
2. Adobe Premiere Pro
3. CorelDRAW
What is a multimedia journalist?
A multimedia journalist is a journalist who uses a variety of media formats like text, photos, videos, audio, graphics, etc. to tell news stories more engagingly and interactively. They gather content through reporting, edit it across multiple platforms, and distribute it to reach wider audiences.
What is a multimedia presentation?
A multimedia presentation integrates different media types like text, images, videos, audio, and animations to present information dynamically and compellingly. It combines visuals, sound, and interactivity to enhance the communication of ideas. Multimedia presentations are used in business, education, marketing, and many other contexts.
What is a multimedia designer?
A multimedia designer is a digital creative who develops multimedia content and products by combining different media formats. They design user interfaces, interactive experiences, websites, apps, digital presentations, etc. using graphics, text, video, audio, and animation. Their goal is to craft impactful and user-friendly content across multiple platforms.

