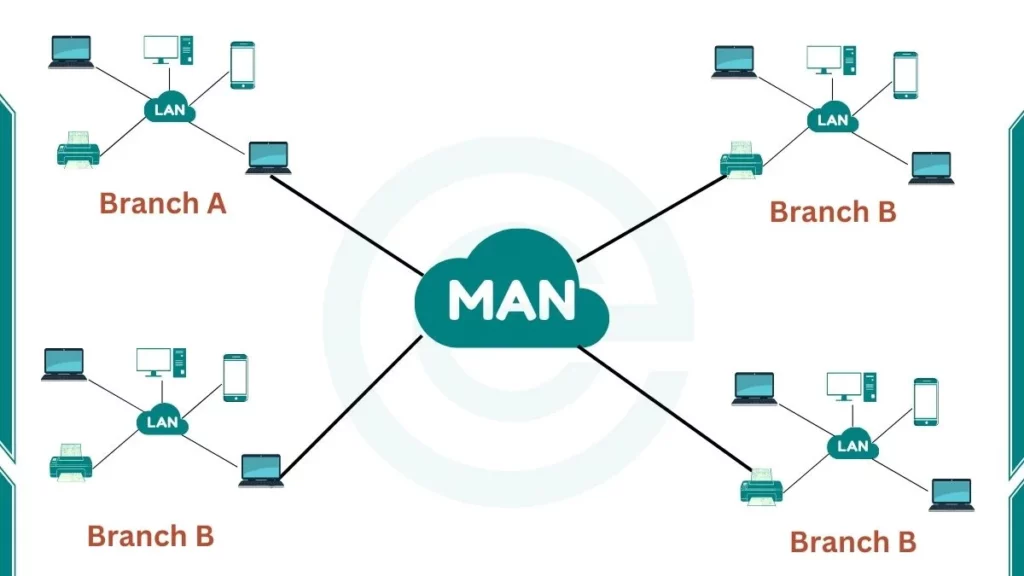
MAN’s full form is Metropolitan Area Network. MAN is a computer network that covers a geographic area of a few kilometers to around 50 kilometers. The term “metropolitan” refers to its size, not necessarily an urban area. MAN network is bigger than a LAN (Local Area Network) but smaller than a WAN (Wide Area Network).
A MAN connects multiple Local Area Networks (LANs) within a city or region, allowing efficient communication and resource sharing. Further, MANs can provide internet access to businesses and institutions.
Features of MAN Network
Here are the key features of metropolitan area network:
- High-Speed Data Transfer: MANs utilize fiber optic cables and advanced technologies to deliver speeds ranging from 1 Gbps to 100 Gbps, ensuring rapid data transmission across the metropolitan area.
- Wide Geographic Coverage: Covers distances from 5 to 50 kilometers, effectively connecting multiple buildings, campuses, or offices within a city or region.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Easily expandable network infrastructure that can accommodate growing demands and additional LANs as organizations expand.
- Centralized Resource Sharing: Enables multiple organizations to share common resources such as servers, printers, scanners, and internet connections efficiently.
- Dual Bus System: Incorporates dual bus architecture that allows data transmission in both directions simultaneously, enhancing network efficiency.
- Multiple Technology Support: Can operate using various link technologies, including Ethernet runs, dark fiber, wireless LAN (WLAN), microwave links, and private 5G networks.
- Dedicated Point-to-Point Connections: Establishes direct backbone connections between locations, reducing latency and improving reliability.
Benefits of MAN
Using a MAN offers many key benefits:
- Efficient data sharing between organizations: Organizations within the same metropolitan area can easily share data and resources through the MAN.
- Improved communication and collaboration: A MAN facilitates seamless communication and collaboration among different entities, such as government agencies, educational institutions, and businesses.
- High-speed Internet access: Businesses and institutions within the MAN can access the Internet at high speeds.
- Cost-effective solution: Building a MAN is more cost-effective than individual organizations setting up their Wide Area Networks (WANs).
Metropolitan Area Network Examples
Here are a few real-life examples of MAN:
- Government agencies: Different government agencies within a city or region can share data and resources through a MAN, improving coordination and efficiency.
- Educational institutions: Schools, colleges, and universities within a metropolitan area can use a MAN to facilitate communication, collaboration, and resource sharing among students, faculty, and staff.
- Healthcare providers: Hospitals and healthcare facilities within a city can securely share patient information and medical data through a MAN, enhancing patient care and coordination.
- Businesses: Companies with multiple offices within a metropolitan area can use a MAN to connect their LANs, enabling efficient data transfer and resource sharing.
How does a MAN Network work?
A MAN connects multiple LANs within a metropolitan area using different technologies such as fiber optic cables and microwave links. It acts as a high-speed data transfer and resource-sharing network, enabling efficient communication and collaboration among the connected LANs.
Common technologies used in MANs include:
- Fiber optic cables: Fiber optic cables are widely used in MANs due to their high bandwidth and data transfer speeds.
- Microwave links: Microwave links are wireless connections that can transmit data over short distances within a metropolitan area.
- Switching and routing devices: MANs use switches and routers to manage and direct network traffic efficiently.
Limitations of MANs
MAN’s also have some limitations:
- Limited geographical coverage: MANs are designed to cover a metropolitan area, typically ranging from a few kilometers to around 50 kilometers. They are not suitable for connecting networks across larger geographical areas.
- Scalability challenges: As the number of connected LANs and devices increases within a MAN, scalability can become an issue, potentially leading to performance bottlenecks and increased complexity in network management.
- Security concerns: With multiple organizations and LANs connected to a MAN, there is an increased risk of security breaches and unauthorized access. It requires robust security measures and policies.
- High initial setup costs: Implementing a MAN can be costly, especially in terms of infrastructure (e.g., fiber optic cables, switching and routing devices) and installation.
- Dependence on service providers: Organizations within a MAN typically rely on service providers for network maintenance, upgrades, and support, which can lead to dependency and potentially higher operating costs.
The Future of MANs
As technology continues to evolve, MANs are also expected to adapt and incorporate new advancements. Some trends and developments that could impact MANs include:
- Growth of smart cities and the Internet of Things (IoT): With the increasing adoption of smart city technologies and the Internet of Things (IoT), MANs will play a crucial role in connecting and managing different devices and systems within a metropolitan area.
- Increased demand for bandwidth and data security: As the amount of data being transmitted grows, there will be a higher demand for increased bandwidth and robust security measures to protect sensitive information.
- Potential for new protocols and network architectures: New protocols and network architectures may emerge to address the evolving needs of MANs, such as higher speeds, better security, and improved scalability.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What technologies are commonly used to build a MAN?
MANs commonly use fiber optic cables (including dark fiber), Carrier Ethernet, MPLS, microwave links, wireless LAN (WLAN), millimeter wave radio, private 5G networks, and switching/routing devices.
What are the main security concerns with MANs?
MANs are vulnerable to cyber-attacks, including man-in-the-middle attacks, distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks, and unauthorized access, due to their multiple connection points.
What is the difference between MAN and Metro Ethernet?
Metro Ethernet is a specific technology used to build MANs, but it is not synonymous with MAN itself. A MAN is the overall network architecture, while Metro Ethernet is one of several technologies (along with MPLS, DWDM, etc.) that can be used to implement a MAN.

