Networking devices, such as gateways and switches help computers communicate. But they work differently. Many students confuse them. Today, we will learn the key differences between a Gateway and a Switch in simple terms.
A Gateway connects different networks, like your home Wi-Fi to the internet. It translates data between different systems. A switch connects devices in the same network, like computers in a lab, and sends data directly to the right device.
What is a Gateway?
A gateway connects two different networks. It acts like a translator. For example, your home router is a gateway. It connects your home network (LAN) to the internet (WAN).
Features of a Gateway:
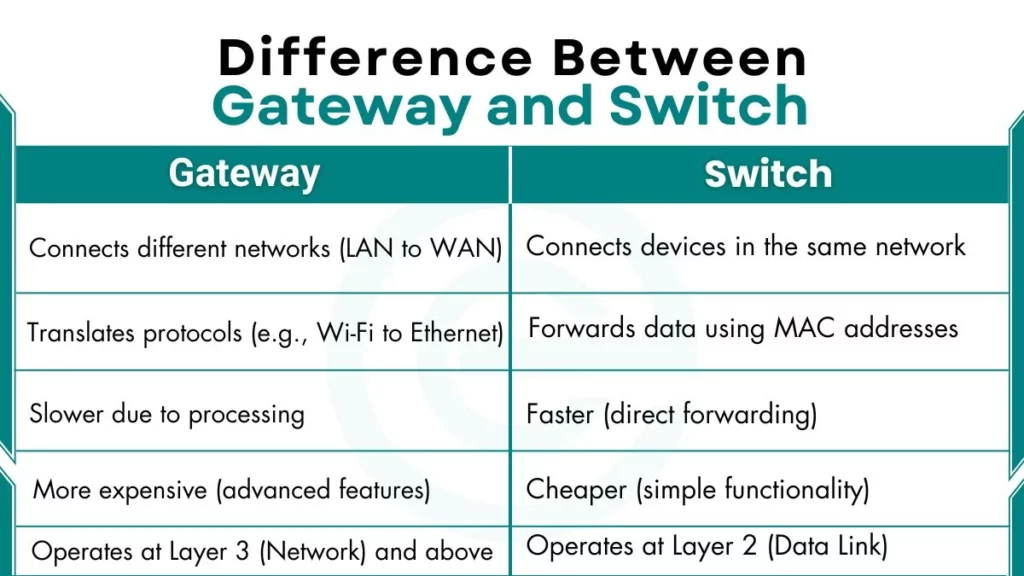
- Works at Layer 3 (Network Layer) or higher.
- Can change data formats (like Wi-Fi to Ethernet).
- Often has security features (firewall, NAT).
- Used in homes, offices, and ISPs.
What is a Switch?
A switch connects devices within the same network. It works like a traffic signal. It sends data only to the correct device using MAC addresses.
Features of a Switch:
- Works at Layer 2 (Data Link Layer).
- Does not change data, only forwards it.
- Used in schools, offices, and data centers.
- Faster than a hub because it avoids unnecessary traffic.
What is Difference Between Gateway and Switch
| Aspect | Gateway | Switch |
|---|---|---|
| Network Layer Operation | Operates at Layer 3 (Network) and above – Handles IP routing between networks | Operates at Layer 2 (Data Link) – Uses MAC addresses for local communication |
| Connectivity Purpose | Connects different networks (LAN-WAN, IPv4-IPv6) | Connects devices within same network (PCs, printers) |
| Data Processing | Inspects/modifies entire packets – Protocol translation – Uses routing tables | Forwards frames based on MAC addresses – Uses MAC address tables – Floods when destination unknown |
| Network Scope | Wide-area connectivity (cities/countries) – Links dissimilar networks | Local connectivity (single building/floor) – Same network type only |
| Configuration | Requires complex setup: IP ranges, firewall rules, routing protocols | Mostly plug-and-play – Optional VLAN configuration |
| Traffic Management | Balances multiple WAN connections – QoS prioritization – Bandwidth shaping | Manages local collisions – Controls broadcast domains – Port-based traffic |
| Security Features | Firewall protection – NAT hiding – VPN endpoints | Port security – MAC filtering – VLAN segmentation |
| Performance | Slower due to deep packet inspection | Faster due to hardware-based switching |
| Typical Location | Network edge (between LAN and WAN) | Inside network (device interconnection) |
| Example Use Cases | Home router to ISP – School district connections – Protocol translation | Computer labs – Office networks – Data center racks |
When to Use a Gateway vs. a Switch?
Use a Gateway When:
- You need to connect two different networks (like a home LAN to the internet).
- You require protocol conversion (like IPv4 to IPv6).
- You need security features (firewall, VPN).
Use a Switch When:
- You want to connect multiple devices to the same network.
- You need fast communication (like in gaming or video streaming).
- You want a simple, low-cost solution for local networking.
FAQs
Can a home router be both a gateway and a switch?
Yes. Most home routers have a built-in switch (for LAN ports) and a gateway (for internet connection).
Does a switch improve Wi-Fi speed?
No, A switch only helps wired connections. For Wi-Fi, you need a better router (gateway) or access point.

