Data communication is the process of sending and receiving data between devices. This exchange happens through various systems, such as computers, phones, or other electronic devices. For example, when you send an email, your computer (sender) transmits data to another computer (receiver) through the internet (transmission medium).
Data communication is not just about sending text messages or emails. It also includes things like video calls, online gaming, and even downloading files. Every time you use the internet, you are using data communication.
Why is Data Communication Important?
Data communication is important because it allows us to share information quickly and efficiently. Without it, we wouldn’t have the internet, mobile networks, or even simple tools like email.
Think about how you use the internet every day. You watch videos, chat with friends, and search for information. All of these activities rely on data communication. It connects people, businesses, and governments around the world.
Examples of Data Communication
- Sending a text message to a friend.
- Watching a video on YouTube.
- Making a video call using apps like Zoom or Skype.
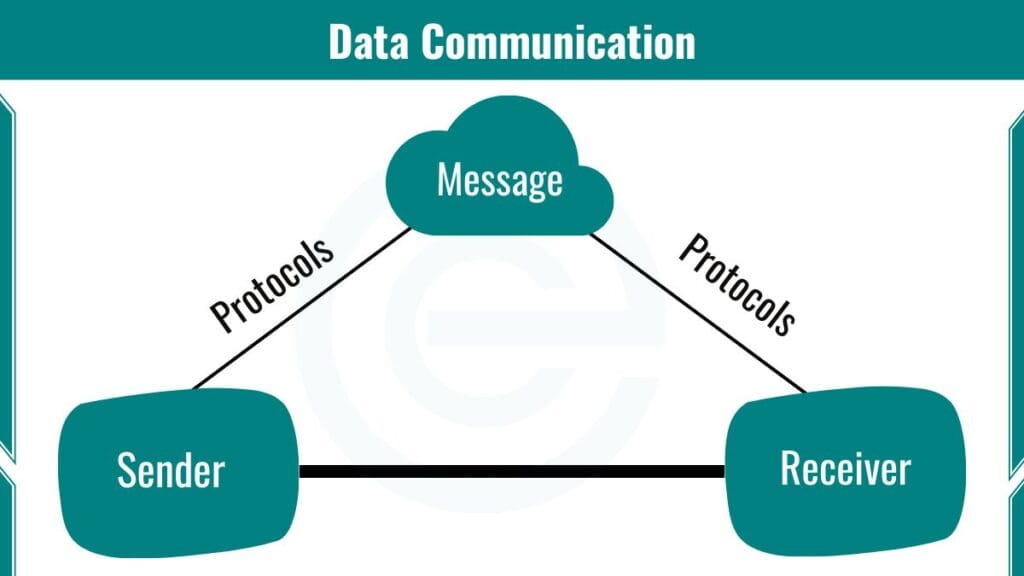
Components of Data Communication
A data communication system consists of five key components:
Message
The message is the data being sent. This could be a text message, an email, or a video. For example, the text you type in a message is the message.
Sender
The sender is the device that sends the data. This could be your smartphone, computer, or any other device. For example, when you send an email, your computer is the sender.
Receiver
The receiver is the device that receives the data. This could be your friend’s smartphone or a server on the internet. For example, when your friend receives your email, their computer is the receiver.
Transmission Medium
The transmission medium is the path through which the data travels. This could be a cable, Wi-Fi, or a mobile network. For example, when you send a text message, the mobile network is the transmission medium.
Protocol
The protocol is a set of rules that govern how the data is transmitted. Protocols ensure that the data is sent and received correctly. Without protocols, devices wouldn’t understand each other. For example, TCP/IP is a protocol used for internet communication.
Data Communication Protocols
Two fundamental protocols in data communication are:
- TCP (Transmission Control Protocol): It takes your message, breaks it into smaller packages (packets), and puts a label on each with the sender and receiver addresses. It ensures they all arrive in the correct order. If a packet goes missing, TCP politely asks for it to be sent again.
- IP (Internet Protocol): Think of IP as the addressing system of the internet. Just like every house has a unique address, every device on a network has a unique IP address. IP makes sure your message doesn’t end up in your neighbour’s inbox!
Types of Data Communication
Data communication can occur in three ways:
- Simplex Communication: Simplex communication is one-way communication. Data flows in one direction only. For example, a keyboard sending data to a monitor is simplex communication.
- Half-Duplex Communication: Half-duplex communication is two-way communication, but not at the same time. Data flows in both directions but only one direction at a time. For example, walkie-talkies use half-duplex communication.
- Full-Duplex Communication: Full-duplex communication is two-way communication that happens simultaneously. Data flows in both directions at the same time. For example, your internet connection allows you to upload and download data at the same time.
Also Read: Difference Between Half-Duplex and Full-Duplex Communication
Transmission Mediums
Data can travel through different types of transmission mediums. These can be wired or wireless.
1. Wired Communication
Wired communication uses cables to transmit data. There are three main types of wired communication:
- Twisted Pair Cable: Used in telephone lines and LANs. It is cheap and easy to install but not very fast.
- Coaxial Cable: Used in TV cables and internet connections. It is faster than twisted pair cable but more expensive.
- Fiber Optic Cable: Uses light to transmit data. It is very fast and reliable but expensive.
2. Wireless Communication
Wireless communication uses signals to transmit data. There are four main types of wireless communication:
- Radio Waves: Used in Wi-Fi and mobile networks. They can travel long distances and pass through walls.
- Microwaves: Used in satellite communication. They can travel very long distances but require a clear line of sight.
- Infrared: Used in remote controls. It is fast but can only travel short distances.
- Satellite Communication: Used for global communication. It is expensive but covers large areas.
Data Communication Networks
Data communication networks connect devices to share data. There are four main types of networks:
1. LAN (Local Area Network): A LAN covers a small area, like a school or home. It connects devices within a limited space, such as computers in a computer lab. LANs are fast and reliable. This makes them ideal for small networks.
2. MAN (Metropolitan Area Network): A MAN covers a large area like a city or campus. It connects multiple LANs within a specific region. For example, a university uses a MAN to link all its buildings and departments.
3. WAN (Wide Area Network): A WAN covers a very large area, like a country or the world. The internet is the largest example of a WAN. WANs connect multiple LANs and MANs over long distances.
4. PAN (Personal Area Network): A PAN is a small network for personal use. It connects devices close to a person, like a phone, laptop, or headphones. For example, Bluetooth connects your phone to wireless headphones in a PAN.
Data Communication Models
There are two main models of data communication:
- OSI Model: The OSI model has 7 layers. It is a conceptual framework for understanding communication.
- TCP/IP Model: The TCP/IP model has 4 layers. It is the practical model used in networking.
Importance of Data Communication
Data communication is crucial in our digital age for several reasons:
- Information Sharing: It enables rapid sharing of information across vast distances. Facilitating global communication and collaboration.
- Business Operations: Modern businesses rely heavily on data communication for everything from internal operations to customer interactions and e-commerce.
- Internet of Things (IoT): Data communication is the foundation of IoT. It allows different devices to interact and share data.
- Scientific Research: It enables the sharing of research data, remote experimentation, and collaboration among scientists worldwide.
- Entertainment: Streaming services, online gaming, and social media platforms all depend on efficient data communication.
FAQs
What are three data communication examples?
1. Sending an email to a friend
2. Making a phone call
3. Watching a live video stream online
what does the term attenuation mean in data communication
Attenuation means the signal gets weaker as it travels. It’s like how your voice gets harder to hear when you’re far away. In data communication, this can happen to electrical or wireless signals over long distances.
what is synchronization in data communication?
Synchronization is about keeping the sender and receiver in step with each other. It’s like making sure two dancers are moving to the same beat. In data communication, it helps ensure that information is sent and received correctly and in the right order.
