A scanning device is an input device that works like a digital camera. Scanning devices examples include Flatbed scanners, Barcode scanners, QR code scanners, MRI scanners, CT scanners, Sheet Feed scanners, Drum Scanners, and more.
Examples of Scanning Devices and their Functions
Here are some scanning device examples:

1. Flatbed Scanner
A flatbed scanner is a familiar sight in homes and offices. It allows you to scan documents, photos, and other flat objects by placing them face down on a glass surface. With their user-friendly design and high-quality image reproduction, flatbed scanners are a popular choice for digitizing paperwork and preserving memories.

2. Handheld Scanner
Handheld scanners are Compact and portable, they offer comfort on the go. Roll or swipe the scanner over the desired surface, instantly capturing text or images. These handy devices are perfect for quickly digitizing notes, receipts, or small sections of larger documents, making them ideal for professionals and students alike.

3. Sheet Feed Scanner
When you need to scan multiple pages, a sheet feed scanner is your go-to solution. These efficient devices automatically feed and scan one page after another, saving you valuable time and effort. Sheet feed scanners are commonly found in busy office environments where high-volume scanning is a regular occurrence.

4. Drum Scanner
In the world of high-resolution imaging, drum scanners reign supreme. These advanced devices employ a rotating drum to capture incredibly detailed scans of photographs, artwork, or other delicate materials. Drum scanners are widely used in the publishing and graphic design industries where precision and accuracy are paramount.

5. Barcode Scanner
Barcode scanners have revolutionized inventory management and retail operations. By simply pointing the scanner at a barcode, these devices can instantly read and record product information, streamlining processes and reducing errors. Whether you’re in a grocery store or a warehouse, barcode scanners are indispensable tools for efficient data collection.

6. QR Code Scanner
Similar to barcode scanners, QR code scanners decode the intricate patterns found in Quick Response (QR) codes. These codes can contain a wealth of information, from website links to contact details, making them a versatile tool for marketing, advertising, and data sharing. With the rise of mobile technology, QR code scanners have become increasingly accessible, often integrated into smartphone cameras.
7. MRI Scanner
In the medical field, MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) scanners play a vital role in diagnostic procedures. These advanced devices use powerful magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed images of the body’s internal structures, helping doctors detect and diagnose various conditions with remarkable accuracy.
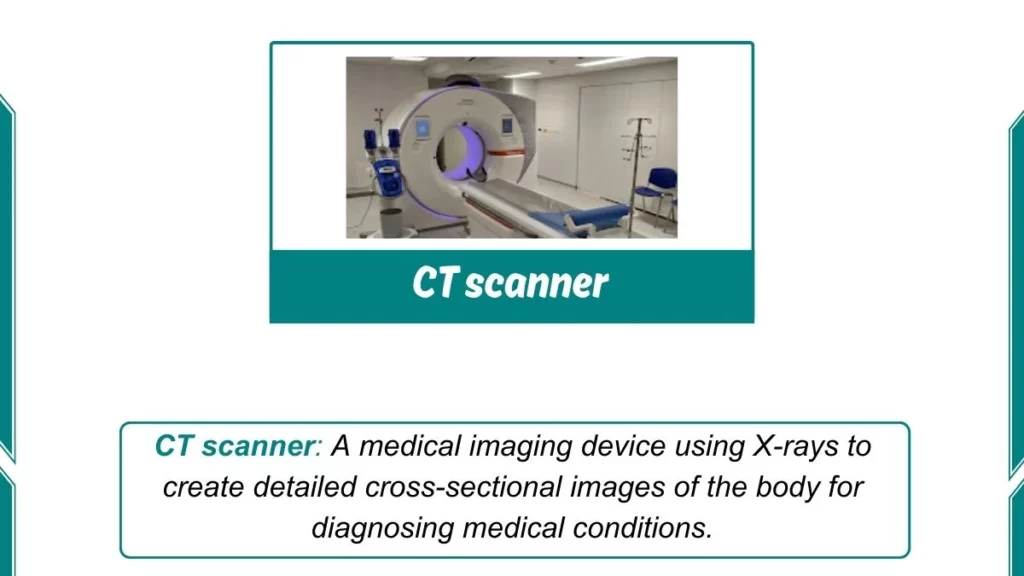
8. CT Scanner
Computed Tomography (CT) scanners are another important medical imaging tool. By combining a series of X-ray images taken from different angles, CT scanners can produce highly detailed cross-sectional views of the body. These scans are invaluable for diagnosing injuries, and diseases, and monitoring the effectiveness of treatments.
9. LiDAR Scanner
LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) scanners are revolutionizing the fields of surveying, mapping, and autonomous vehicle technology. These devices use laser beams to measure distances and create highly accurate 3D representations of their surroundings.
LiDAR scanners are instrumental in applications such as urban planning, environmental monitoring, and self-driving car navigation.

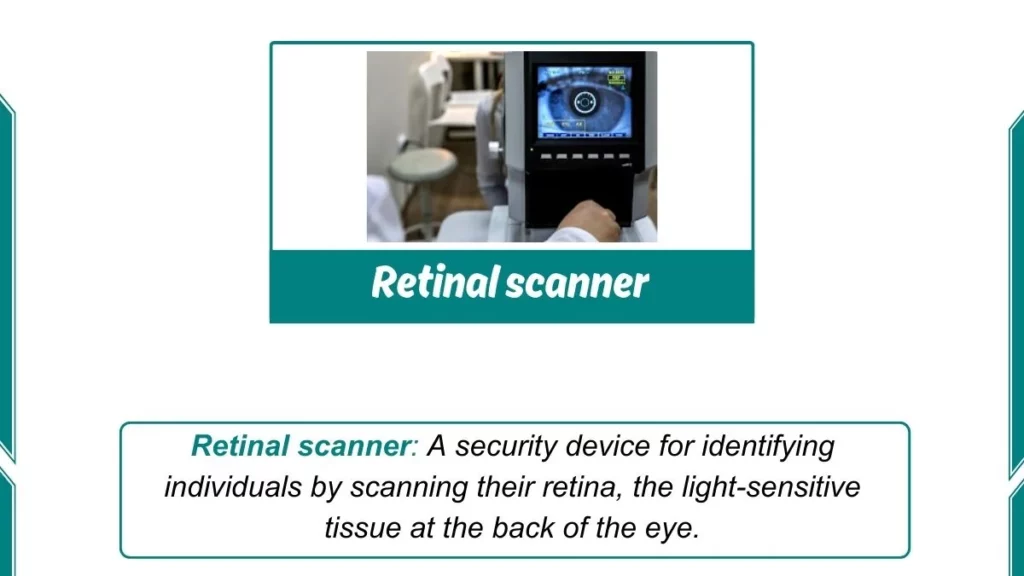
10. Retinal Scanner
Retinal scanners are sophisticated biometric devices that analyze the unique patterns of a person’s retina for identification purposes. These scanners are commonly used in high-security environments, such as government facilities or financial institutions, where maintaining strict access control is paramount.
By leveraging the inherent uniqueness of each individual’s retina, retinal scanners offer an extremely reliable and secure method of authentication.