A search engine is a tool that helps people find online information. It scans countless websites to deliver the most relevant results based on a user’s query, or search term.
Search engines are crucial in the digital age because they allow quick access to endless amounts of information. Search engines can lead you to answers, tutorials, videos, news, and more with just a few words.
Did You Know?
The term “search engine” first became popular in the early 1990s with the launch of basic web search tools. Today, they help people find everything from simple answers to complex research data.
History of Search Engines
Here is the history of search engines:
Early Development
The concept of a search engine began with Archie in 1990, which indexed files on the web. In 1994, search engines like Yahoo and Lycos began indexing entire web pages.
Evolution Over Time
- 1994: Yahoo launches as a directory.
- 1998: Google revolutionizes search with its PageRank algorithm.
- 2005: Google introduces personalized search based on user history.
- 2015: Mobile search surpasses desktop, marking a shift to mobile-first indexing.
Types of Search Engines
Here are the different types of search engines:
1. General Search Engines
These are the most common types of search engines and are used by millions every day. Examples include Google, Bing, and Yahoo. They cover a wide range of information and are not limited to any specific topic.
2. Specialized Search Engines
Some search engines focus on specific types of content. For example, Google Scholar is designed for academic papers and research articles, while Pinterest specializes in images.
Specialized search engines are valuable for finding particular information more easily than general search engines.
3. Meta Search Engines
A meta search engine doesn’t have its index but instead collects results from other search engines. Examples include Dogpile and MetaCrawler. Meta search engines gather information from several sources and display a combined results list.
How Search Engines Work?
The below steps explain how search engines work:
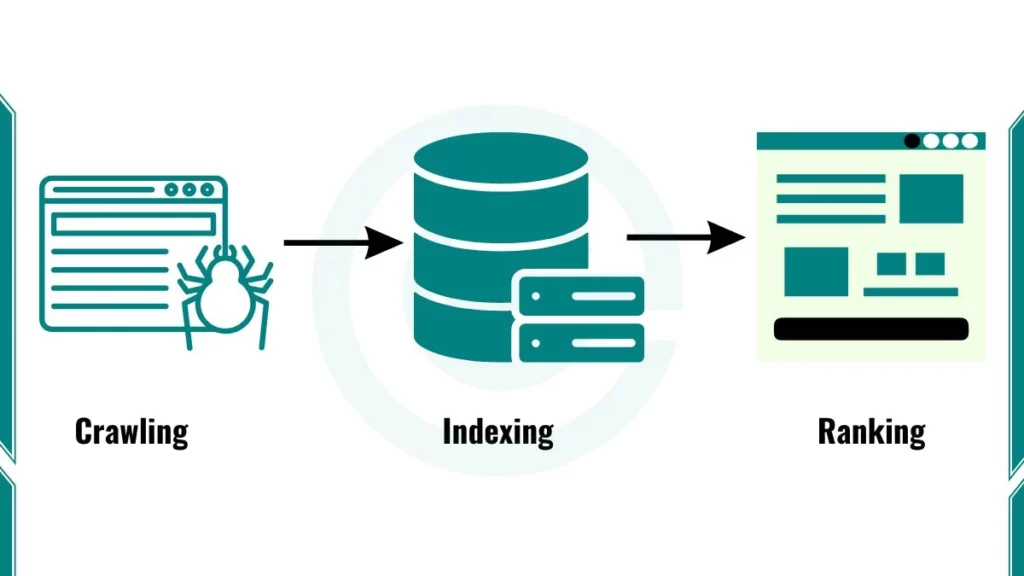
1. Crawling and Indexing
Search engines rely on special programs called web crawlers or spiders to scan the internet. These crawlers follow links and scan content on web pages. After finding content, they store it in an index a massive database. The index allows search engines to locate content quickly whenever someone searches for related terms.
2. Search Algorithms
An algorithm is a set of rules search engines use to determine which results to show for each query. Each search engine has its unique algorithm. Google, for example, uses a sophisticated algorithm that analyzes hundreds of factors to decide the most relevant results.
3. Ranking Factors
Search engines show results by looking at various factors. Some key factors include keywords, backlinks, and content quality. Keywords are the words users type in the search bar; if these match well with page content, they show that page to a user. Backlinks, or links from other sites, show that a page is trusted by others, helping it rank better.
Search Engine Tools and Features
Search engines also have features and tools. Some are mentioned below:
Advanced Search Operators
Operators can make searches more precise:
- Quotes (“ ”): Search for an exact phrase.
- Minus (-): Exclude specific terms (e.g., “apple -fruit”).
- site: Find pages within a particular site (e.g., “site.com”).
Image, News, and Map Searches
Most search engines support media-specific searches:
- Image Search: Google Images, Pinterest
- News Search: Filter news stories by recency or source
- Maps Integration: Google Maps and Bing Maps for location-based results
Try It Yourself: Use the search operator
site:wikipedia.org “World War II”to find Wikipedia pages focused on World War II.
Popular Search Engines Comparison
Here’s a quick comparison of the major search engines examples:
| Search Engine | Market Share | Unique Features |
|---|---|---|
| 91.9% | Rich snippets, image search, maps | |
| Bing | 2.8% | Visual search, integration with Microsoft |
| Yahoo | 1.3% | News aggregator, customizable homepage |
| Baidu | Popular in China | Emphasis on Chinese language search |
| Yandex | Popular in Russia | Localized search for Russian users |
Future Trends in Search Engines
The following are the future trends in search engines:
AI and Machine Learning
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are transforming search engines. AI helps search engines understand language better, improving search results’ relevance. Machine Learning allows the algorithm to improve based on user feedback, creating smarter search results.
Voice Search and Virtual Assistants
With the rise of voice search, many people now use their voices to search. Virtual assistants like Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant have made voice search a common practice. Voice search changes how people interact with search engines, as they often use more conversational language, which is something search engines are adapting to.
Did You Know? Voice search queries are typically longer and more conversational, such as asking “What’s the weather like today?” instead of typing “weather.”
Multiple-choice questions (MCQs)
1. What is the primary function of a search engine?
A) To create websites
B) To scan websites and deliver relevant results
C) To store user data
D) To sell products
Correct Answer: B) To scan websites and deliver relevant results
2. When did the term “search engine” first become popular?
A) 1980s
B) Early 1990s
C) Late 1990s
D) 2000s
Correct Answer: B) Early 1990s
3. Which search engine revolutionized the search process with its PageRank algorithm?
A) Yahoo
B) Bing
C) Google
D) DuckDuckGo
Correct Answer: C) Google
4. What type of search engine focuses on specific types of content?
A) General Search Engines
B) Meta Search Engines
C) Specialized Search Engines
D) Directory Search Engines
Correct Answer: C) Specialized Search Engines
5. What do web crawlers or spiders do in the search engine process?
A) Create websites
B) Scan and index web content
C) Store user preferences
D) Display search results
Correct Answer: B) Scan and index web content
6. Which of the following is a key ranking factor for search engines?
A) Website design
B) Keywords
C) Page color
D) User location
Correct Answer: B) Keywords
7. What is the purpose of using advanced search operators?
A) To create websites
B) To make searches more precise
C) To track user activity
D) To improve website speed
Correct Answer: B) To make searches more precise
8. What unique feature does Bing offer compared to other search engines?
A) Rich snippets
B) Visual search
C) News aggregation
D) Backlink analysis
Correct Answer: B) Visual search
9. How is AI transforming search engines?
A) By creating more websites
B) By making them slower
C) By helping them understand language better
D) By decreasing user interaction
Correct Answer: C) By helping them understand language better
10. What types of queries are typically longer and more conversational?
A) Text-based queries
B) Voice search queries
C) Image search queries
D) Meta-search queries
Correct Answer: B) Voice search queries
