A web application is a software program that runs on a web server and is accessed through a web browser. Unlike a traditional website that mainly displays information, a web application enables users to perform interactive tasks. Web applications are widely used in daily operations such as email, social networking, online banking, and document management.
Components of Web Application
A web application consists of three main components:
1. Frontend (Client-side)
The frontend is the part of a web application that users directly interact with. It includes the user interface (UI) and user experience (UX) elements. Common frontend technologies include:
- HTML: Structures the content on web pages.
- CSS: Defines the style, layout, and appearance.
- JavaScript: Adds interactivity and dynamic behavior.
2. Backend (Server-side)
The backend handles the application’s logic, processes requests, and manages communication with the database. The backend processes user input, performs necessary operations, and sends the response to the frontend. Popular backend technologies include:
- PHP
- Python
- Node.js
- Ruby on Rails
3. Database
A database stores, retrieves, and manages application data. Common databases used in web applications include:
- MySQL
- MongoDB
- PostgreSQL
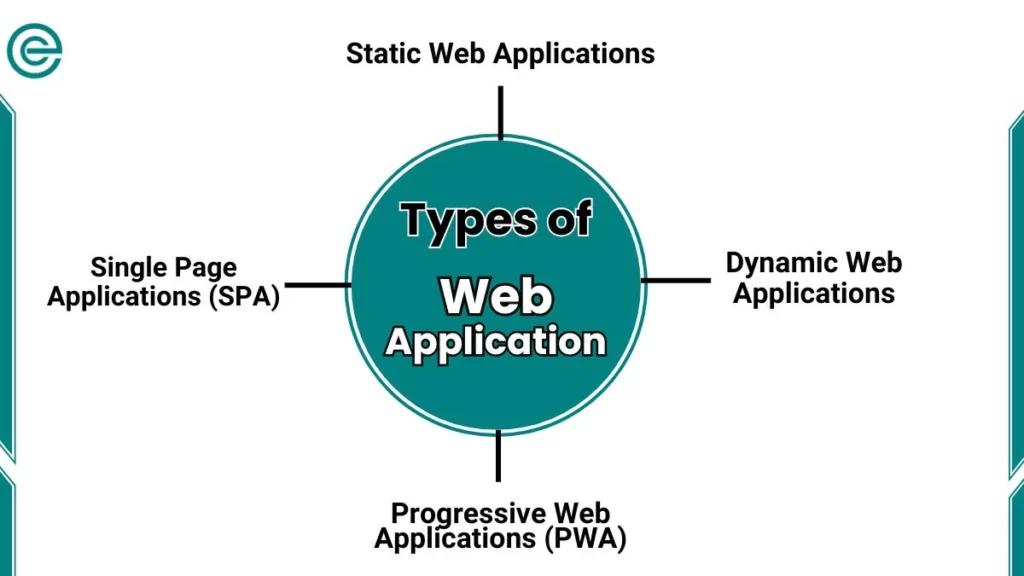
Types of Web Applications
Web applications can be categorized based on functionality and interactivity:
1. Static Web Applications
Static web applications display fixed content that does not change unless the developer updates the files manually.
- These applications are built using HTML, CSS, and basic JavaScript.
- They do not interact with databases for dynamic content.
- They load quickly because the content is delivered as pre-built files.
- Suitable for simple websites such as portfolios or company profiles.
2. Dynamic Web Applications
Dynamic web applications generate content in real time based on user actions or server-side processing.
- They use server-side languages such as PHP, Python, or Node.js.
- The content changes according to user inputs or database queries.
- They often include interactive features such as forms, dashboards, and user accounts.
- Suitable for websites that require frequent data updates.
3. Single Page Applications (SPA)
Single Page Applications load the initial page once and update content dynamically without reloading the entire page.
- They rely heavily on JavaScript frameworks such as React, Angular, or Vue.
- Only specific components update when users interact with the page.
- They provide a faster and smoother user experience.
- Common examples include email services and project management tools.
4. Progressive Web Applications (PWA)
Progressive Web Applications combine web technologies with native app-like features.
- They support offline access using service workers.
- They load quickly even on low network conditions.
- Users can install them on their device like a mobile app.
- Suitable for websites that require improved performance and mobile accessibility.
How Web Applications Work
The working of a web application typically involves the following steps:
- The user sends a request through a web browser.
- The server receives and processes the request.
- The server interacts with the database when required.
- The processed response is sent back to the browser.
- The browser displays the result to the user.
APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) often facilitate communication between different components or external services, enhancing functionality and integration.
Advantages of Web Applications
- Accessible from any device with a web browser
- Cross-platform compatibility
- Centralized updates without installation
- Efficient data management
Disadvantages of Web Applications
- Dependence on internet connectivity
- Potential security risks without proper protection
- Limited performance for high-resource tasks
Examples of Popular Web Applications
- Gmail: Email communication platform
- Google Docs: Online document creation and editing
- Facebook / Instagram: Social media networking
- Online Banking Portals: Secure financial transactions
For more information read our detail article on Web Application examples.
Difference Between Web Application, Website, and Mobile Application
| Feature | Website | Web Application | Mobile Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Information | Interaction & tasks | Interaction on mobile |
| Access | Browser | Browser | Installed app |
| Updates | Periodic | Centralized, instant | Requires installation |
| Example | Wikipedia | Gmail |
FAQs
What is the main purpose of a web application?
A web application enables users to perform interactive operations such as submitting forms, editing documents, or managing data through a browser.
Do web applications require installation?
No, web applications run directly in a browser and do not require installation.
How is a web application different from a regular website?
A website mainly displays information, while a web application allows users to perform interactive tasks.

