A motherboard socket is a crucial part of a computer’s motherboard. It is the place where the CPU (Central Processing Unit) connects to the motherboard. This connection allows the CPU to communicate with other components of the computer. The CPU cannot work, and the computer will not function without a proper socket.
Function of a Motherboard Socket
The motherboard socket holds the CPU firmly in place. It ensures that the CPU aligns correctly with the motherboard. This alignment is vital for the CPU to send and receive data efficiently. Without a proper socket, the CPU cannot function or interact with other components.
Here are some of its key functions:
- Holds the CPU Securely
- Provides Electrical Connections
- Enables Data Transfer
- Supports Cooling Solutions
Types of Motherboard Sockets
The following are different types of motherboard sockets with their function:
1. Pin Grid Array (PGA)
In a PGA socket, the CPU has small pins that fit into holes in the motherboard socket. This design is used by AMD processors.
PGA sockets provide a secure connection between the CPU and the motherboard. The pins inside the socket create an electrical connection with the CPU to allow data to flow between them.
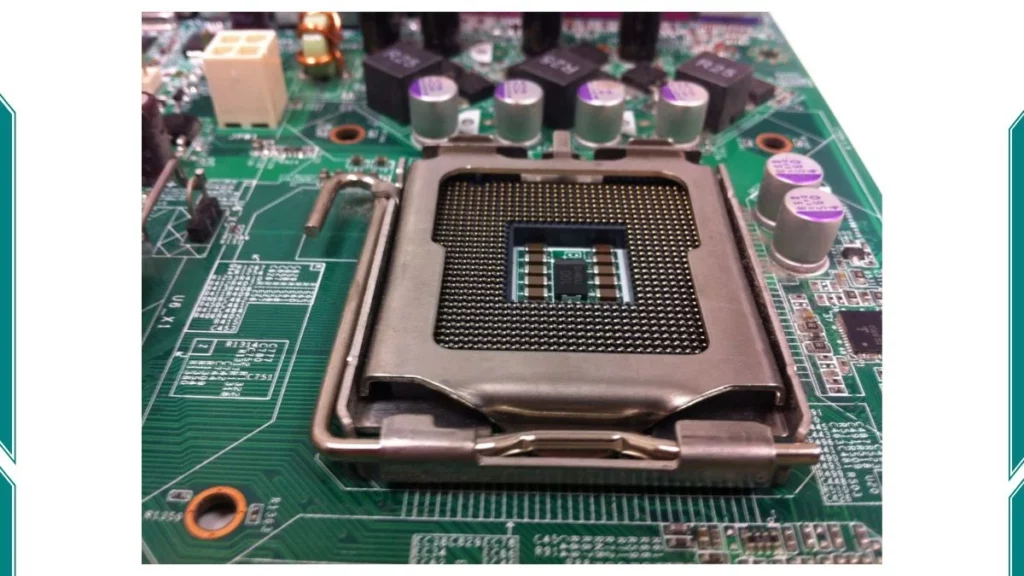
2. Land Grid Array (LGA)
The LGA socket is the opposite of the PGA. In LGA, the motherboard has pins that touch the CPU’s flat pads. The CPU has no pins but instead has small pads that connect with the motherboard’s pins.
LGA sockets offer better stability and can handle more pins and electrical connections than PGA sockets. The flat pads of the CPU make better contact with the motherboard’s pins, which improves power delivery and data transfer.
3. Ball Grid Array (BGA)
BGA sockets are not removable. The CPU is directly soldered onto the motherboard. This means the CPU is permanently attached to the motherboard and cannot be removed or replaced easily.
This design reduces space, making it ideal for portable devices. It also limits the ability to upgrade or replace the CPU.
What is a CPU Socket?
The CPU socket is a special area on the motherboard where the CPU is placed. It holds the CPU securely and ensures that it connects properly to the other components. The socket has tiny pins or holes that match the CPU’s design. This connection allows the CPU to send and receive data from the rest of the system.
For a visual explanation, you can watch the following video:
FAQs
Can you replace a motherboard socket?
Replacing a motherboard socket is complex and usually not practical. If a socket is damaged, it’s often best to replace the entire motherboard.
Why are sockets important for computer performance?
Sockets determine which CPUs can be used. It affects the computer’s speed and capabilities. Choosing the right socket ensures optimal performance.
Why are BGA sockets not common in desktops?
BGA sockets are designed for small devices like laptops. They are not removable, which makes them less flexible for upgrades.
