Every day, you interact with two types of documents without even thinking about it. You read a printed textbook in class that is a hard copy. You open a PDF on your phone that is a soft copy. Both carry the same information, but they exist in completely different forms.
I remember asking my students to submit their class assignments. Half of them walked in with printed sheets. The other half shared Google Docs links. That single moment in my classroom perfectly shows the hard copy vs soft copy divide we discuss in theory. This article focuses entirely on the differences between them.
What is a Hard Copy?
A hard copy is a physical and tangible output of information that was originally stored or created in digital form. It exists in the real, material world. You can touch it, hold it, and store it in a physical space like a drawer or a filing cabinet.
In computer science, a hard copy is also referred to as a permanent copy because it remains intact even when the computer is turned off. Once it is printed, it stays as it is. The most common hard copy is a printed document on paper.
What is a Soft Copy?
A soft copy is a digital and intangible version of a document or file. It exists in electronic form and can only be viewed through a device such as a computer, tablet, smartphone, or projector. You cannot physically touch a soft copy. It only exists as data stored in binary form.
Soft copies are also called temporary copies in some contexts. For example, a file open in RAM (Random Access Memory) is a soft copy that disappears when you close the program or turn off the device. However, when saved to a hard drive or the cloud, it becomes a permanent digital file.
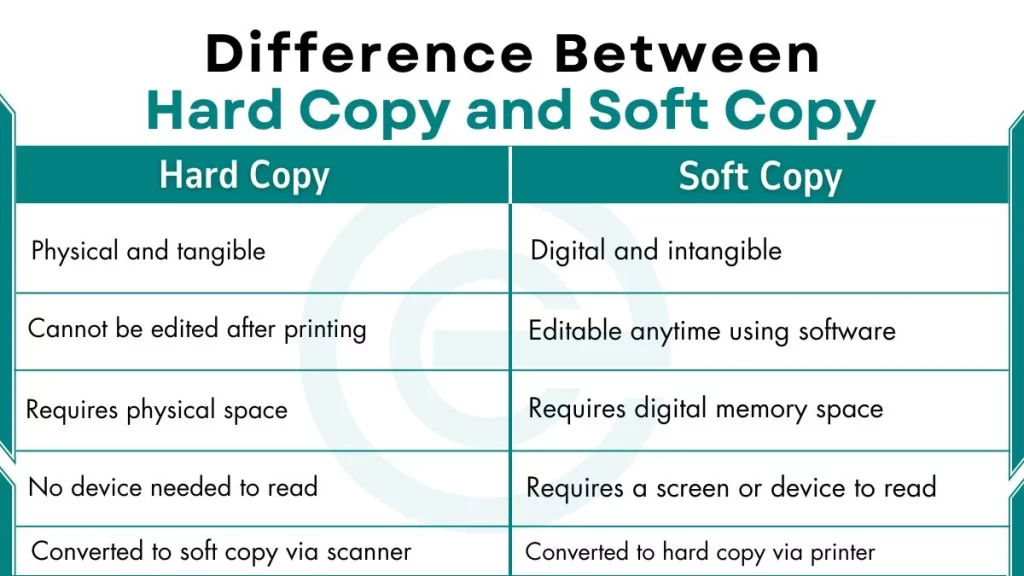
Difference Between Soft Copy and Hard Copy
Here is a detailed comparison between hard copy and soft copy to better understand:
| Parameter | Hard Copy | Soft Copy |
|---|---|---|
| Form | Physical and tangible | Digital and intangible |
| Nature | Permanent and fixed | Temporary and flexible |
| Storage Medium | Paper, cardboard, film | HDD, SSD, USB drive, cloud |
| Editability | Cannot be edited after printing | Editable anytime using software |
| Portability | Bulky and heavy | Lightweight and highly portable |
| Sharing Method | Physical delivery or courier | Email, cloud link, messaging apps |
| Sharing Speed | Hours, days, or weeks | Seconds or minutes |
| Output Device | Printer, Plotter, Laser Printer | Monitor, Projector, Screen |
| Input Device to Create | Scanner (to digitize) | Keyboard, mouse, stylus |
| Cost per Document | High (paper + ink + printer) | Very low or near zero |
| Storage Space | Requires physical space | Requires digital memory space |
| Durability Risk | Fire, water, and physical wear | Virus, corruption, accidental deletion |
| Backup Process | Manual photocopying | Automatic cloud or disk backup |
| Environmental Impact | Uses paper, ink, and chemicals | More eco-friendly, less waste |
| Security Type | Physical lock, cabinet, seal | Password, encryption, access control |
| Security Vulnerability | Physical theft, photocopying | Hacking, phishing, malware |
| Accessibility | Requires physical presence | Accessible from any device globally |
| Search and Navigation | Manual page-by-page search | Instant keyword search using Ctrl+F |
| Readability | No device needed to read | Requires a screen or device |
| Format | Fixed layout after printing | Flexible — zoom, resize, reformat |
| Multiple Copies | Each copy requires printing | Unlimited copies with one click |
| Transmission Distance | Limited by geography | No geographical limitation |
| Life Span | Degrades over time | Lasts as long as storage is maintained |
| Official/Legal Use | Widely accepted for legal documents | Acceptance is growing but varies by country |
| Annotation | Manual, pen or pencil | Digital, comments, highlights, sticky notes |
| Version Control | Not possible | Possible using tools like Google Docs or Git |
| File Format | Not applicable | PDF, DOCX, XLSX, PPTX, EPUB, TXT |
| Conversion | Converted to soft copy via scanner | Converted to hard copy via printer |
| Internet Required | Not required | Required for cloud access only |
| Power Dependency | Not required after printing | Requires power to view on a device |
| Collaboration | Not possible in real time | Real-time collaboration via Google Docs, OneDrive |
| Space Efficiency | 1 filing cabinet ≈ ~2,000 pages | 1 TB drive ≈ millions of documents |
| Examples | Printed book, newspaper, certificate | PDF, eBook, Word document, email |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Can a soft copy become a hard copy?
Yes. You convert a soft copy into a hard copy by printing it using a printer or plotter.
What devices produce hard copy output?
Printers, laser printers, inkjet printers, and plotters all produce hard copy output. These are classified as hard copy output devices in computer science.
Is a PDF a hard copy or soft copy?
A PDF is a soft copy. It is a digital file that you view on a screen. If you print a PDF on paper, that printed version becomes a hard copy.

