The main difference between edge and cloud computing is that edge computing processes data locally on devices or nearby servers. This makes it faster for real-time tasks like gaming or smart devices. On the other hand, Cloud computing relies on remote data centers over the internet, which is better for storage-heavy jobs like streaming or backups. Edge works offline, while cloud needs constant internet.
Edge Computing
Edge computing processes data closer to where it is created, like on your phone, a smartwatch, or a traffic sensor. Instead of sending data far away, it gets processed nearby for faster results.
Examples:
- Self-driving cars (process road data instantly).
- Smart home devices (like Alexa responding quickly).
- Fitness trackers (analyze your steps without the cloud).
Cloud Computing
Cloud computing means storing and processing data on remote servers over the internet. Instead of using your computer’s hard drive, you use powerful computers (servers) located in data centers far away.
Examples:
- Google Drive (stores your files online).
- Netflix (streams movies from remote servers).
- Zoom (runs video calls using cloud servers).
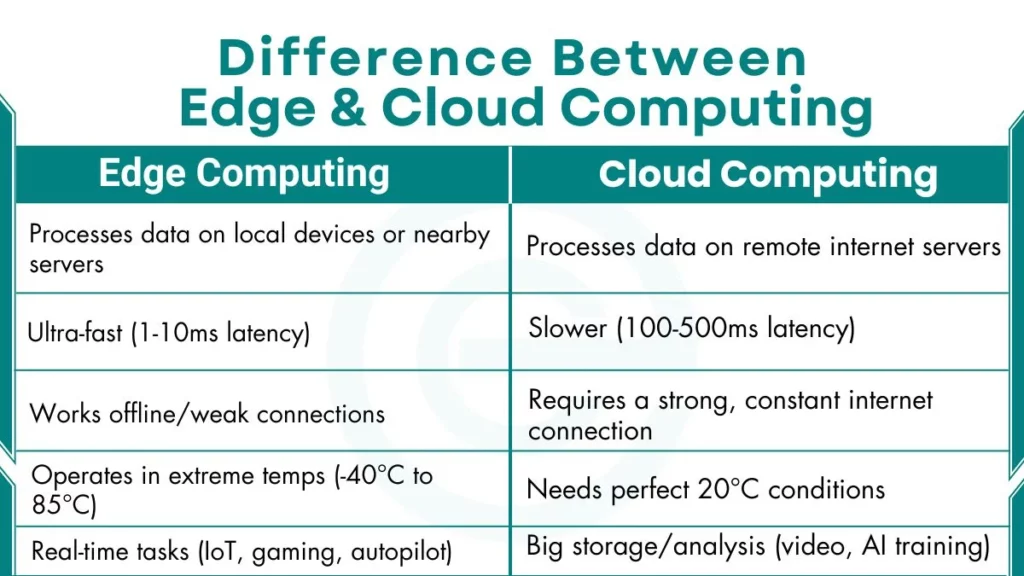
Differences Between Edge and Cloud Computing
The following table shows the difference in detail for better understanding.
| Category | Edge Computing | Cloud Computing |
|---|---|---|
| Basic Definition | Processes data on local devices or nearby servers | Processes data on remote internet servers |
| Speed | Ultra-fast (1-10ms latency) | Slower (100-500ms latency) |
| Internet Requirement | Works offline/weak connections | Requires a strong, constant internet connection |
| Hardware | Small devices (sensors, Raspberry Pi) | Massive server farms |
| Cost Structure | High upfront device costs | Pay-as-you-go monthly fees |
| Data Control | You own all data | Provider controls your data |
| Security | Harder to attack (distributed) | Centralized = hacker target |
| Best For | Real-time tasks (IoT, gaming, autopilot) | Big storage/analysis (video, AI training) |
| Energy Use | Very low (watts) | Extremely high (megawatts) |
| Failure Impact | Only affects local device | Can crash global services |
| Temperature Tolerance | Operates in extreme temps (-40°C to 85°C) | Needs perfect 20°C conditions |
| Maintenance | Manual updates per device | Automatic centralized updates |
| Storage Capacity | Limited (device-dependent) | Virtually unlimited |
| Startup Time | Instant (microseconds) | Seconds to minutes |
| Regulations | Fewer compliance rules | Strict laws (GDPR, HIPAA) |
| Career Skills | Electronics/embedded systems | Web/software development |
| Future Growth | Expanding 30% yearly (IoT boom) | Growing 15% yearly (maturing tech) |
Difference in Special Cases
The following table tells which one is a better choice according to some scenarios.
| Scenario | Better Choice | Why? |
|---|---|---|
| Mars rover operations | Edge | No internet connection possible |
| Global video streaming | Cloud | Needs massive storage distribution |
| Smart factory robots | Edge | Requires instant response times |
| Medical research database | Cloud | Stores/analyzes millions of patient records |
| Self-driving car | Hybrid (Both) | Edge for instant decisions + Cloud for map updates |
FAQs
Can edge computing replace cloud computing?
No, they work best together. Cloud handles big storage, while edge handles fast responses.
Is 5G related to edge computing?
Yes! Faster 5G networks help edge devices process data even quickly.
Which is more secure: cloud or edge?
Edge is usually more secure because less data is sent online. But both need strong security measures.

