Interfaces are the bridge between humans and machines. They make it possible for users to interact with technology easily. Examples of computer interfaces are Graphic User Interfaces (GUI), Command-Line Interfaces (CLI), Touch User Interfaces, and more, which we will examine in this article.
Examples of Interface
The following are examples of computer interfaces:
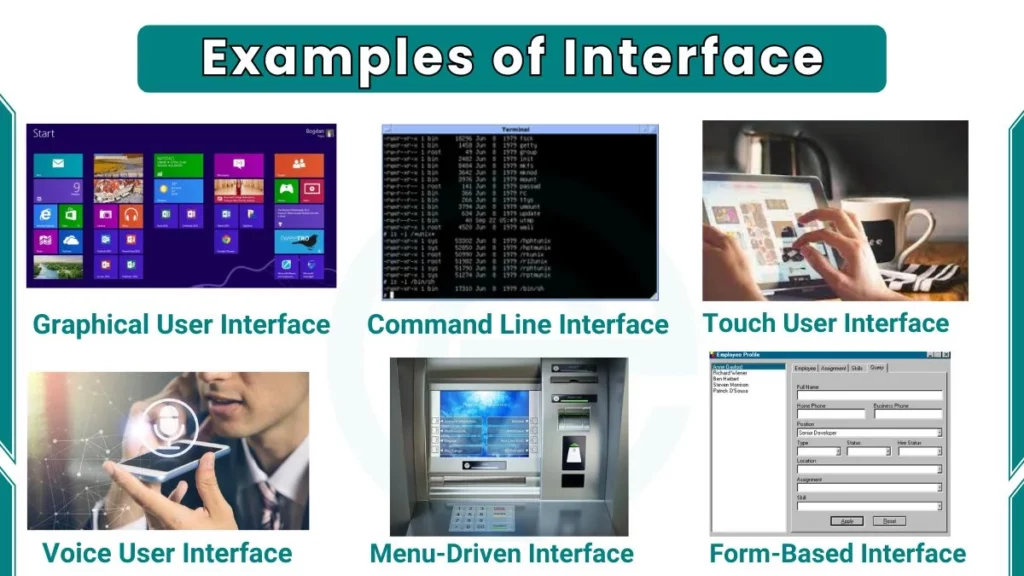
1. Graphical User Interface (GUI)
A Graphical User Interface (GUI) is the most common interface example. It uses visual elements like icons, buttons, and menus. Users perform actions by clicking or tapping. This makes it user-friendly and easy to navigate.
Example: Operating systems like Windows and macOS.
2. Command Line Interface (CLI)
A Command-Line Interface allows users to type commands to control the computer. It does not have visual elements like a GUI. Instead, users input text commands to operate the system. This interface is faster and more efficient for advanced users. However, it requires knowledge of specific commands.
Examples: The Linux terminal or MS-DOS.
3. Touch User Interface
A Touch User Interface allows users to interact with devices by touching the screen. Gestures like tapping, swiping, and pinching are used for navigation. This interface is intuitive and popular in portable devices. Touch interfaces have replaced traditional buttons in many modern gadgets.
Examples: Smartphones, tablets, and touch-enabled laptops.
4. Voice User Interface (VUI)
A Voice User Interface allows users to give commands by speaking. It is widely used in smart devices and virtual assistants. Users can ask questions, set reminders, or control smart homes using their voice.
Examples are virtual assistants like Alexa, Google Assistant, or Siri.
5. Natural Language Interface
Natural Language Interfaces enable users to interact with computers in everyday language. These interfaces understand and process natural sentences, making them ideal for casual users. It helps search and ask questions.
Example: Chatbots and search engines with natural language processing.
6. Menu-Driven Interface
Menu-driven interfaces provide a list of options in the form of a menu. Users navigate the menu to select their desired action. This interface is simple and widely used in devices with limited input methods and automated systems.
Example: ATMs or settings menus on phones.
7. Adaptive User Interface
An Adaptive Interface changes based on user preferences or behaviour. It learns from the user’s actions and adjusts accordingly, making the interface more personalized and efficient.
Example: Personalized dashboards on learning platforms or streaming services.
8. Gesture-Based Interface
Gesture-Based Interfaces use physical movements to interact with devices. Sensors detect gestures like hand waves or body movements. These interfaces are widely used in gaming and virtual environments.
Example: Gaming systems like Xbox Kinect or VR headsets.
9. Form-Based Interface
A Form-Based Interface displays forms with fields for users to fill in. It is structured and straightforward and often used for collecting data.
Example: Online registration forms or survey tools.
10. Hardware-Based Interface
Hardware-based interfaces involve direct interaction with physical devices. Users operate buttons, knobs, or touch panels on hardware. These interfaces are simple and often specific to the device.
Example: Printer control panels or gaming consoles.
11. Brain-Computer Interface (BCI)
A Brain-Computer Interface connects computers directly to the human brain. It reads brain signals to control devices. This interface is used in advanced technologies, especially in medical fields.
Example: Prosthetic control systems.
12. Multimodal Interface
Multimodal interfaces allow users to interact using multiple input methods, including touch, voice, gestures, or even eye movements. Such interfaces offer flexibility and convenience.
Example: Car infotainment systems or smart home devices.
13. Augmented Reality (AR) Interface
An Augmented Reality Interface overlays digital elements onto the real world. Users can simultaneously see and interact with physical and virtual environments, making this interface engaging and educational.
Example: AR apps or smart glasses.
14. Virtual Reality (VR) Interface
Virtual Reality Interfaces create a wholly digital environment. Users wear devices like VR headsets to enter this virtual space. These interfaces are immersive and are commonly used in gaming and training.
Example: VR headsets used in gaming or education.
15. Text-Based Interface
A Text-Based Interface uses text for input and output. It is simple but has limitations in performing complex tasks. Text-based interfaces were standard in older computers and are still used in some basic systems.
Example: Early web pages or basic software prompts.

